Color Wheel

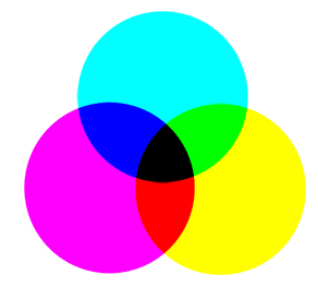
CMYK
CMYK is used for print. It stands for Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, and Black pigment in used in 4-color process printing. Also referred to as full color printing. CMYK is used that creates all other colors. It’s a subtractive process, as more color is used, the more light is removed or absorbed to create the color. Cyan, Magenta, and yellow combined create a dark brown, adding k or black completely removes all light. Our eyes read this as black.
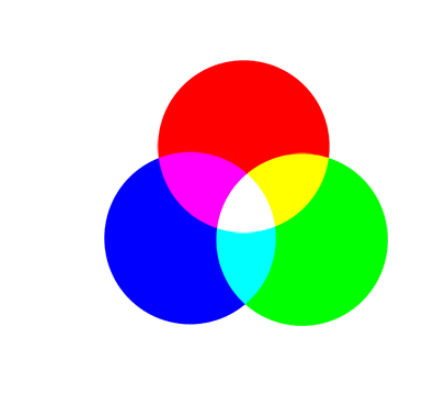
RGB
Red, Green and Blue is associated with our electronic device displays, monitors, tablets, Pen tablet displays, cell phones, and digital cameras, RGB is supported in all browsers. Each parameter is between 0-255. (W3School, n.d.). RGB W3Schools offers a RGB calculator to experiment with the thousands of colors that can be created by using R,G,B.
Hue
A hue can be referred to as one of the primary (Red, Yellow and Blue) and secondary colors (Orange, Green, and Violet) of the color wheel. Hues refer to the underlying base color of a color mixture. White, Grey and Black are not included as a hue.

Chroma
Chroma is sometimes referred to as saturation, purity or color intensity. Chroma is the vividness of a color. High chrome is free of white, grey and black. Chroma can be measured in absolute on the Munsell Color Scale. Munsell Color Scale is a three-dimensional scale based on three properties of color measuring hue (Basic Color) Chroma (color intensity) and value (lightness).

Tints
A tint is a hue mixed with pure white. Sometimes they are referred to as pastels, but the true definition of a tint is adding white to the pigment. A tint lightens the color but does not brighten the hue.

Tone
A tone is a hue mixed with gray. The gray is created by mixing white and black, not a neutral gray that is created with a color. The gray will tone the hue. As gray is added, the duller the hue becomes.
Shades
Shades are created by mixing black with any hue. The black darkens the hue. The more black added, the darker the hue becomes until the hue is no longer detectable in the shade.

Tertiary Colors
There are six tertiary colors. Each tertiary color is made by mixing a primary color with an adjacent secondary color on the color wheel: yellow-orange, red-orange, red-violet, blue-violet, blue-green, and yellow-green.
Monochromatic Colors
Monochromatic Color Scheme uses tints, tones and shades of color on the color wheel.
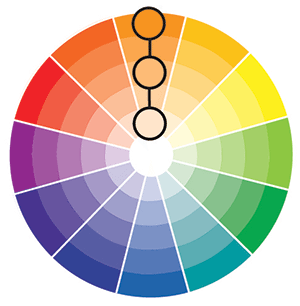
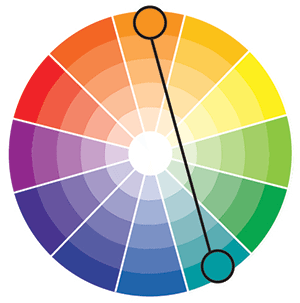
Complementary Colors
Complementary color scheme uses colors that are opposite on the color wheel.
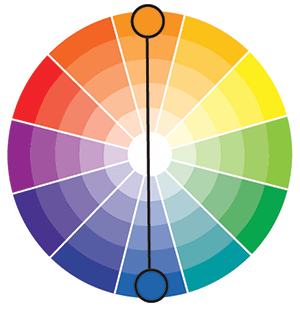
Split Complementary Colors
To create a Split Complementary color scheme, start by choosing a color. Then choosing two colors on either side of the opposite of the first color on the color wheel.
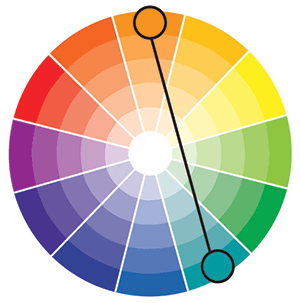
Analogous Colors
Analogous Color Scheme are the use of two to five colors that are adjacent to each other on the color wheel.
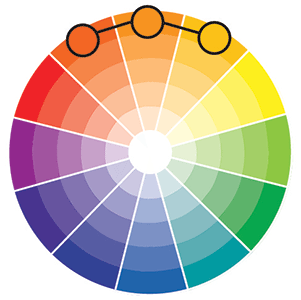
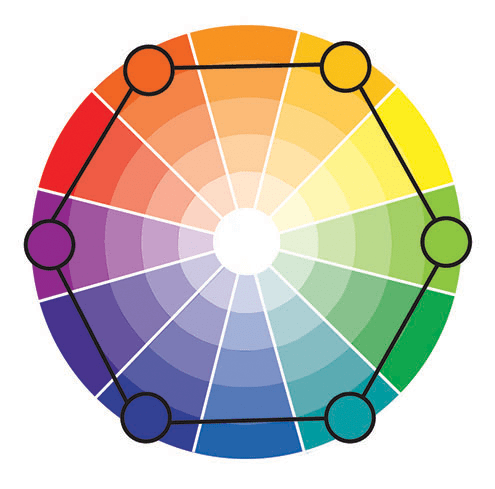
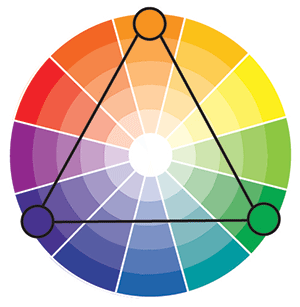
Triad Colors
Triad uses three colors equally spaced from each other on the color wheel.
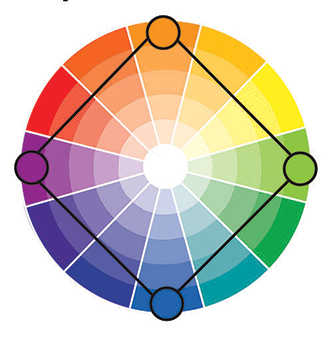
Double Complementary Colors (Rectangle Tetradic)
The Double Complementary color scheme uses four colors arranged into two complementary pairs. This color scheme offers many varieties. When using this color scheme, one color should be the dominant color while the others are secondary.
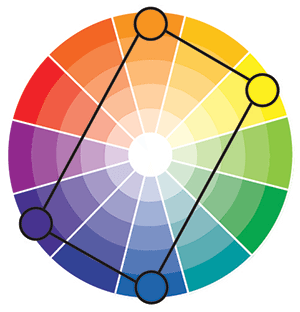
Double Split Complementary Colors (Pentagonal)
Double Split Complementary uses a combination of colors that contain two sets of complements like red and green or blue and orange.
Side Complementary Colors
Using a color in combination with another color on either side of its complement on the color wheel.
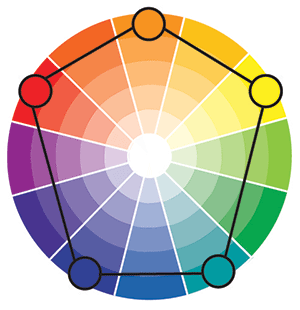
Square Tetradic Color
A Square Tetradic color scheme uses four colors arranged into two complementary pairs. There is a balance between warm and cool colors. The square color scheme is evenly spaced around the color circle.
MISSION STATEMENT
The art of building brands - start to finish™
-
Google Ads & Analytics Certified
-
30+ years, award-winning graphic designer
-
Email marketing & automation expert (Klaviyo, Mailchimp, HubSpot)
-
Social media strategy & content systems
-
Local SEO & Google Business Profile optimization
-
Corporate branding & identity systems
-
Print marketing & production (brochures, packaging, signage)